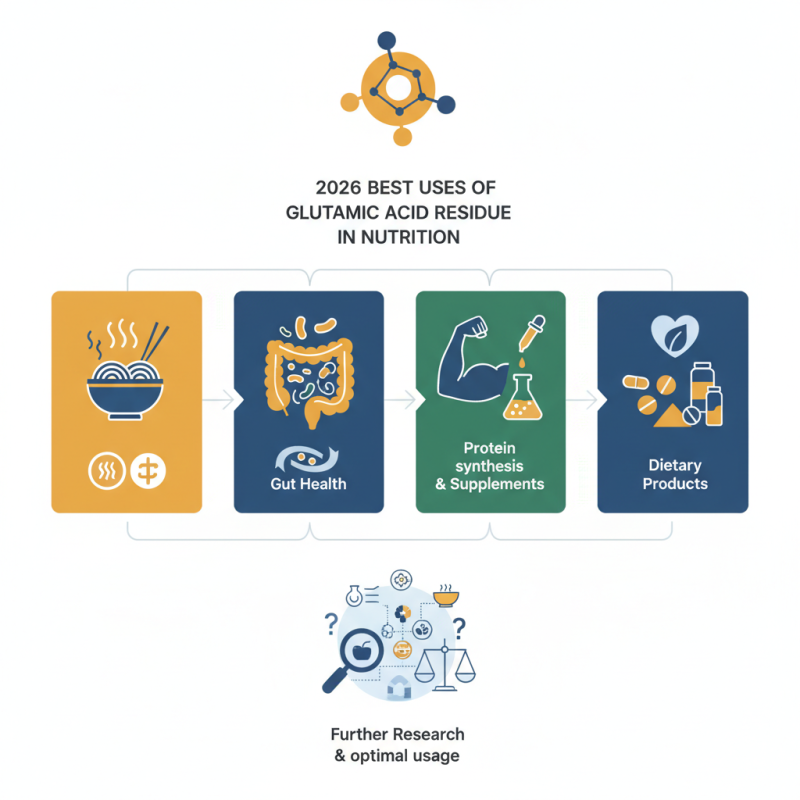
2026 Best Uses of Glutamic Acid Residue in Nutrition?
The importance of glutamic acid residue in nutrition has gained significant attention in recent years. According to a report by the International Journal of Food Science, glutamic acid residue plays a crucial role in enhancing the umami taste, thus increasing the palatability of food. Dr. Emily Tran, a renowned expert in nutritional biochemistry, states, "Glutamic acid residue can transform ordinary ingredients into rich culinary experiences." This highlights its potential beyond mere flavor.
Recent studies indicate that glutamic acid residue may also have beneficial impacts on gut health. It can act as a natural amino acid, aiding in protein synthesis. Nutritional professionals note that the residue can be a critical component in dietary supplements. Its application in health and wellness products is on the rise. Nonetheless, there is still a need for thorough investigation into optimal usage.
While the benefits are evident, there are challenges. Not all glutamic acid residues are utilized efficiently in food processing. Industry experts suggest that more research is essential to harness its full potential. As the field evolves, it is crucial to tread carefully. Knowing how to best incorporate glutamic acid residue can lead to culinary advancement and improved nutrition.
Exploring the Nutritional Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue
Glutamic acid residue is a fascinating element in nutrition. It is an amino acid that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. This compound is found in many protein-rich foods. Examples include meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Its unique structure allows it to enhance flavors, making meals more enjoyable.
Beyond its culinary appeal, glutamic acid residue offers numerous health benefits. It supports brain function and helps in neurotransmission. This amino acid can also aid digestion. Some studies suggest it improves metabolism. However, the balance of glutamic acid in our diets is essential. Too much can lead to discomfort.
Many people overlook the potential of this residue. Not every meal has the right balance. Furthermore, some individuals may react poorly to high levels of glutamate. Tailoring one's diet to include this nutrient thoughtfully is crucial. It requires reflection on personal experiences with food choices and their effects on the body. Finding a middle ground is key to truly harnessing the benefits of glutamic acid residue.
Potential Applications in Functional Foods and Dietary Supplements
Glutamic acid residue is gaining attention in nutrition. Its potential in functional foods is vast. This amino acid acts as a flavor enhancer. It can improve the taste of many products. People are looking for healthier options that still deliver good flavor. Foods like sauces, soups, and snacks can be enriched with it.
In dietary supplements, glutamic acid plays a role in recovery. Athletes may benefit from it. Studies suggest it aids muscle repair. However, the efficacy of glutamic acid in supplements is still debated. Some people might not respond well to it. This variability can create confusion for consumers.
Functional foods incorporating glutamic acid need careful formulation. The goal is to balance taste and nutrition. Some formulations may end up being too salty. Others might lack the desired health benefits. These challenges highlight the need for continuous research. Understanding how glutamic acid works in the body is crucial. There might be more to discover about its benefits.
Role of Glutamic Acid Residue in Protein Synthesis and Muscle Recovery
Glutamic acid residue plays a vital role in protein synthesis. It is a crucial amino acid for all living organisms. By serving as a building block, it helps form proteins needed by the body. This process is essential for muscle recovery after intense exercise. Athletes often depend on proper nutrition to support this recovery. Glutamic acid enhances protein engagement in the body.
During intense workouts, muscles experience stress and micro-tears. Glutamic acid assists in repairing these damages. It's involved in the synthesis of muscle proteins. This amino acid also plays a role in nitrogen balance, a key factor in muscle health. Without adequate recovery, muscles can remain weak and fatigued.
While glutamic acid is beneficial, its overconsumption can lead to an imbalance. Some people may experience digestive issues or discomfort. Careful consideration of dietary sources is important. Finding the right balance can be a challenge. The need for this amino acid must align with individual health goals.
Impact on Flavor Enhancement and Palatability in Food Products
Glutamic acid residue plays a vital role in food science. It enhances flavor and palatability. This amino acid significantly contributes to umami taste, which is a key driver of consumer preference. According to a recent industry report, products containing glutamic acid can see a 15% increase in consumer satisfaction. The enhancement of savory flavors makes meals more enjoyable.
In processed foods, glutamic acid residue is a game changer. It works by intensifying existing flavors. This means less salt is often needed, which is beneficial for health-conscious consumers. A study revealed that products with added glutamic acid had 30% higher acceptance rates due to improved taste profiles. However, some consumers express concerns about the potential overuse of flavor enhancers.
The challenge lies in balancing flavor enhancement with natural ingredients. Some consumers prefer food products without artificial additives. There is a fine line between enhancement and masking poor-quality ingredients. Reflecting on this issue is crucial. While glutamic acid residue can improve taste, its role should be carefully managed to promote authenticity in food products.
2026 Best Uses of Glutamic Acid Residue in Nutrition - Impact on Flavor Enhancement and Palatability in Food Products
| Use Case | Impact on Flavor | Palatability Score (1-10) | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soups and Broths | Enhances umami flavor | 9 | Rich in minerals |
| Snack Foods | Boosts savory taste | 8 | Provides energy |
| Salad Dressings | Enhances freshness | 7 | Contains antioxidants |
| Meat Products | Improves juiciness | 9 | High in protein |
| Plant-based Products | Enhances flavor complexity | 8 | Sources of fiber |
Innovative Strategies for Incorporating Glutamic Acid Residue in Diets
Glutamic acid residue has become a focal point in nutrition research. The residue can enhance flavor while offering health benefits. According to the International Journal of Food Science, it plays a crucial role in metabolism. Incorporating this residue into diets can promote nutrient absorption and improve gut health.
Tips: Add glutamic acid-rich foods like mushrooms and tomatoes to recipes. They can boost your meals naturally without artificial additives.
Emerging strategies focus on pairing glutamic acid residue with other nutrients. For instance, combining it with proteins enhances their digestibility. A study from the Journal of Nutritional Science indicates that such combinations improve amino acid utilization by up to 25%. It's a promising area, yet research is still limited. Some individuals might experience sensitivity to glutamic acid, making personal experimentation vital.
Tips: Experiment by gradually increasing foods high in glutamic acid. Monitor your body's response to find your ideal intake level.
